Unveiling the Kubernetes Resume Challenge: A Quest for Professional Growth - Part 2

Edward Allen Mercado
Posted on March 3, 2024

As we embark on the second leg of our journey, it's time to take another step towards conquering the Kubernetes Resume Challenge!
In Part 1, we laid the groundwork, setting up our Kubernetes cluster, configuring services, and preparing our database which covers the Step 1 to 5.
Please join me again as we navigate through the challenges and triumphs that lie ahead, inching closer into completing this quest.
Implementation
Step 6: Implement Configuration Management
In this step, our objective is to create a ConfigMap with the data of FEATURE_DARK_MODE set to true. Subsequently, we'll need to adjust our app/ code to accommodate this configuration by adapting to the value of the Environment Variable. Finally, we'll modify our website Deployment to include the ConfigMap.
We'll implement the Dark Mode feature by creating a separate .css file specifically for this mode. Our approach involves verifying that the Environment Variable FEATURE_DARK_MODE is set to true. Once confirmed, we'll render the dark mode style by linking the appropriate .css file in our application.
Step 7: Scale Your Application
In this phase, we'll evaluate the scalability of our application. Can it gracefully handle increased traffic without manual intervention?
To simulate a scale-up scenario, execute the following command:
kubectl scale deployment/<website_deployment_name> --replicas=6
This command increases the number of Pods in your Deployment to 6. You can monitor the growing number of Pods by running:
kubectl get po -w
Once the scaling operation is complete, see if the newly created Pods are in Running State, then navigate to our website endpoint and verify if it behaves as expected, without any errors, despite the increased resources.
Step 8: Perform a Rolling Update
In this phase, we'll enhance our website by adding a promotional banner to the body of our web pages as part of our marketing campaign. To accomplish this, we'll need to modify the code in the app/ directory accordingly. Once the changes are made, we'll rebuild and push our Docker image with the new tag v2 to our Docker Hub repository.
After updating the Docker image, we'll need to ensure that our website Deployment is using the latest version. We can achieve this by either deleting and recreating the Deployment or by executing the set image command:
kubectl set image deployment/<web_deployment_name> <container_name>=<your_docker_repo>:<new_tag>
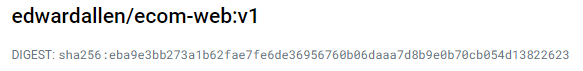
In my experience, there have been cases where changes made to the Docker image are not immediately reflected, even when referring to the correct tags. This can occur if we're constantly pushing changes to the same Docker tag, such as v1, without incrementing it. To mitigate this issue, I recommend using the sha of the Docker image instead, as it points to the most recent changes pushed to your Docker repository. You can find this sha output in your repository or every time you push the image via the command line.
v1: digest: sha256:eba9e3bb273a1b62fae7fe6de36956760b06daaa7d8b9e0b70cb054d13822623 size: 5113
Step 9: Roll Back a Deployment
Uh-oh! It seems that the banner we recently deployed has introduced a bug to our website. To rectify this issue, we'll need to roll back the deployment to a previous state.
You can accomplish this by executing the following command:
kubectl rollout undo deployment/<website_deployment_name>
Once the rollout completes successfully, verify if the website returns to its previous state, without the banner, ensuring that the bug has been resolved.
Step 10: Autoscale Your Application
Now that we've observed how our website behaves under increased traffic and during rollbacks, it's time to implement autoscaling to ensure optimal performance under varying workloads. To achieve this, we'll utilize the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler resource.
Simply execute the following command to implement autoscaling:
kubectl autoscale deployment <website_deployment_name> --cpu-percent=50 --min=2 --max=10.
To verify that the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler is functioning as expected, we can use tools like Apache Bench to generate traffic to our endpoint. First, install Apache Bench and generate load to your Website Endpoint using the command:
ab -n 100 -c 10 <website_endpoint>
You can monitor the behavior of the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler and your Pods by executing the following commands in separate command line tabs or windows:
kubectl get hpa -w
kubectl get pod -w
This allows you to observe how the autoscaler adjusts the number of Pods based on the generated load, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
Step 11: Implement Liveness and Readiness Probes
In this phase, we'll enhance the reliability of our website by adding liveness and readiness probes. These probes ensure that before our website starts running, it is verified as working, and it maintains its operational state throughout its lifecycle.
To achieve this, we'll modify the Deployment definition to include these probes and then recreate our Deployment.
In my case, I've utilized specific path and separate php files to verify their functionality, such as /db_healthcheck.php and healthcheck.php.
If you'd like to try this on my website endpoint, simply append the mentioned path to the URL.
This implementation ensures that our website is always responsive and maintains its availability, contributing to a seamless user experience.
Step 12: Utilize ConfigMaps and Secrets
In this phase, we revisit the implementation of our database and website to ensure secure management of database connection strings and feature toggles without hardcoding them in the application.
As previously mentioned, we've already stored these database connection strings and configurations either in an Environment Variable or a ConfigMap, requiring only minor adjustments.
To enhance security, we'll ensure that sensitive data is stored using Secrets, while non-sensitive information can remain in a ConfigMap.
We'll then modify the Deployment definition to include both ConfigMap and Secrets, and subsequently recreate our Deployment.
This approach ensures that our application's sensitive information remains protected, contributing to a more robust and secure deployment.
Conclusion
And there we have it, we've successfully completed the challenge! I hope you found value in following along with my blog.
I'm immensely grateful for the opportunity to tackle this challenge, as it not only tested my technical skills but also fostered personal growth and resilience. The satisfaction of overcoming each hurdle and witnessing the evolution of my project fills me with a sense of accomplishment and pride.
For me, this journey doesn't end here. I've also taken on the extra steps mentioned in the challenge, so stay tuned if you're interested in continuing to explore this challenge further with me!
Before we embark further into our next journey, I invite you to stay connected with me on social media platforms. Follow along on Twitter, LinkedIn.

Posted on March 3, 2024
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.