Hands-On Coding: Exploring Hyperparameters for Programmers

Ed Legaspi
Posted on March 7, 2024
Introduction
In this article, we will explore different techniques for finding the optimal hyperparameter values from a given set of parameters in a grid. Particularly we will look at RandomizedSearchCV, GridSearchCV, and BayesSearchCV.
In this blog you will learn:
- How to initialize the parameter grid.
- How to find the optimal hyperparameters based on a given technique.
- How to build a model (XGBClassifier) to use the hyperparameters.
- How to score the performance of the model.
RandomizedSearchCV
param_grid = {
"gamma": [0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 6, 12, 20],
"learning_rate": [0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.8],
"max_depth": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12],
"n_estimators": [25, 50, 65, 80, 100, 115, 200]
}
grid_search = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=classifier_0, param_distributions=param_grid, scoring=scoring)
GridSearchCV
param_grid = {
"gamma": [0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 6, 12, 20],
"learning_rate": [0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.8],
"max_depth": [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12],
"n_estimators": [25, 50, 65, 80, 100, 115, 200]
}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(estimator=classifier_0, param_grid=param_grid, scoring=scoring)
BayesSearchCV
param_bayes = {
'gamma': Categorical(param_grid['gamma']),
'learning_rate': Categorical(param_grid['learning_rate']),
'max_depth': Categorical(param_grid['max_depth']),
'n_estimators': Categorical(param_grid['n_estimators'])
}
grid_search = BayesSearchCV(estimator=classifier_0, search_spaces=param_bayes, scoring=scoring, n_jobs=-1, cv=10)
Finding the Best HyperParameters
best_model = grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
hyperparams = best_model.best_params_
Building and Scoring the Classifier using the HyperParameters
# Fitting the Model
ne = hyperparams['n_estimators']
lr = hyperparams['learning_rate']
md = hyperparams['max_depth']
gm = hyperparams['gamma']
print("Recommended Params >>", f"ne: {ne},", f"lr: {lr}", f"md: {md}", f"gm: {gm}")
# Build Classification Model
classifier_1 = XGBClassifier(
base_score=0.5,
colsample_bylevel=1,
colsample_bynode=1,
objective=objective,
booster="gbtree",
eval_metric=eval_metric_list,
n_estimators=ne,
learning_rate=lr,
max_depth=md,
gamma=gm,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=1,
random_state=1
)
# Fit Model
eval_set = [(X_train, y_train)]
classifier_1.fit(
X_train,
y_train,
eval_set=eval_set,
verbose=False
)
# Get predictions for training data
train_yhat = classifier_1.predict(X_train)
print("Training Preds: \n", train_yhat[:5])
# Set K-Fold Cross Validation Levels
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
# Training Results
train_results = cross_val_score(classifier_1, X_train, y_train, scoring=scoring, cv=cv, n_jobs=1)
# Brief Review of Training Results
print("Average Accuracy K-Fold: ", round(train_results.mean(), 2))
print("Std Deviation K-Fold: ", round(train_results.std(), 2))
print("Precision Score 0: ", round(precision_score(y_train, train_yhat, average=None)[0], 3))
print("Precision Score 1: ", round(precision_score(y_train, train_yhat, average=None)[1], 3))
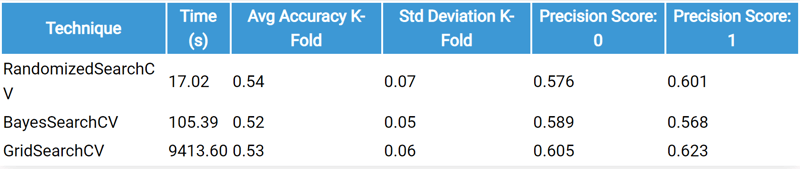
Performance
Machine: Laptop
Processor: AMD Ryzen 7
OS: Windows
DataFrame Shape: (7282, 17)
💖 💪 🙅 🚩

Ed Legaspi
Posted on March 7, 2024
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.