Test Driven Development (TDD) for Smart Contracts

Simon
Posted on September 24, 2022

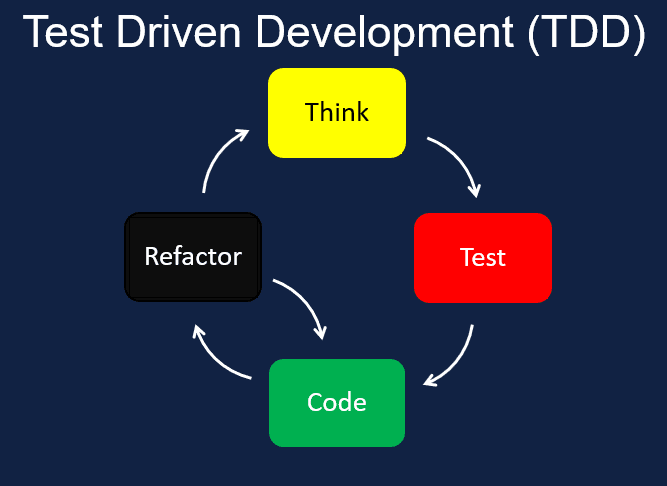
"Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development process relying on software requirements being converted to test cases before the software is fully developed, and tracking all software development by repeatedly testing the software against all test cases." - Wikipedia
A lot of big words, here's the summary of what the above paragraph says: We simply write our tests before writing the code and then we improve the code.
So before implementing a feature, we create the test that describes what we expect that new addition to the software to do so we can write code that ensures the feature does exactly that.
Developing good and maintainable software is important in every domain but extremely crucial when creating Decentralized Applications and Smart Contracts.
Our focus on this article will be TDD but in the end, you'll also be able to retrieve the price of a cryptocurrency in a decentralized fashion. let's get to it!
What are We Building?
We'll be creating a simple project that gets the price of a crypto asset: Ether (ETH).
What Tools Are We Using?
You should have node.js on your machine, you can install it here if you don't.
- Hardhat: A Development and Deployment Environment for Ethereum Software.
- Chainlink A Oracle network for retrieving real-world data in a decentralized manner.
- Alchemy A set of web3 development tools to build and scale your dApp.
Before getting to coding, just a quick note on Chainlink.
What is Chainlink
The main benefits of Blockchain are Decentralization and Immutability, so our smart contracts can't be altered by a central authority or entity but these smart contracts need real-world data to work, things like what the current weather of a city is, what the current price of an asset is, or what team won a soccer game.
Getting this data from a central body defeats the purpose of a blockchain which is decentralization as that body could alter the data being sent to smart contracts in their favor. So we also need to get the data in a decentralized way too.
This is where Chainlink comes in, it gets this data without us having to sacrifice decentralization.

Now that we know what that is, let's get to coding!
Project Setup
First, create a new directory and initialize it by running
$ mkdir tdd-data-feed && cd tdd-data-feed && yarn init
After that is done, you should be in a new folder with a package.json file. We're first going to install hardhat and chainlink.
$ yarn add --dev hardhat dotenv && yarn add @chainlink/contracts
Once hardhat is installed, execute this to install every other dependency.
$ yarn hardhat

You should see something similar to this, select the typescript option and respond y to the rest.
Getting Keys
Create an account on Alchemy to get a new app. After signing up, you should automatically be assigned some apps by Alchemy, you can create one if you weren't given the apps.
Copy the HTTPS key of the Ethereum Main net app.
Create a .env file at the project root and add your key there. Ensure you add .env on your .gitignore file so you don't accidentally leak your keys to Github or any other VCS.
Our First Test
We'll be building everything from scratch so delete the sample files provided in the /contract, /test, and scripts folders.
Now create a new file /test/priceFeed.ts and add this to it:
import { expect } from "chai";
import { Contract } from "ethers";
import { ethers } from "hardhat";
describe("Price Feed", () => {
it("Gets the PriceFeed contract", async () => {
const PriceFeed = await ethers.getContractFactory("PriceFeed");
expect(PriceFeed);
});
});
What we're doing is describing "Price Feed", we expect it to be able to retrieve a contract. Save and run yarn hardhat test.
It failed as expected, there's no PriceFeed contract yet so let's make this test pass. Create a new file contracts/PriceFeed.sol and add this to it.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract PriceFeed {
constructor() {}
}
Now time to pass that test! save and run yarn hardhat test again.
Yay! It's always satisfying to see that green. Our test passed because we were to get the contract PriceFeed which is defined in PriceFeed.sol!
Test 2
Alright, we'll write our next test. This test checks to see if the deployed contract has a state variable ethPriceFeed. We expect this test to fail.
import { expect } from "chai";
import { Contract } from "ethers";
import { ethers } from "hardhat";
describe("Price Feed", () => {
let priceFeed: Contract;
beforeEach(async () => {
// This function runs before each test, this way we don't have to redeploy
// the contract for every single test case.
const PriceFeedFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory("PriceFeed");
priceFeed = await PriceFeedFactory.deploy();
});
it("Gets the PriceFeed contract", async () => {
const PriceFeed = await ethers.getContractFactory("PriceFeed");
expect(PriceFeed);
});
it("Has the Ether Price Feed Aggregator", async () => {
const ethPriceFeed = await priceFeed.getEthPriceFeed();
expect(ethPriceFeed);
});
});
Running the yarn hardhat test command causes this to fail because the getEthPriceFeed function doesn't exist yet so let's create it and make this test green!
Edit your contracts/PriceFeed.sol file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/interfaces/AggregatorV3Interface.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract PriceFeed {
AggregatorV3Interface internal ethPriceFeed;
/**
* Network: Mainnet
* Aggregator: ETH/USD
* Address: 0x5f4eC3Df9cbd43714FE2740f5E3616155c5b8419
* You can get the addresses for more networks and more tokens here at the
* chainlink docs: https://docs.chain.link/docs/reference-contracts/
*/
constructor() {
ethPriceFeed = AggregatorV3Interface(
0x5f4eC3Df9cbd43714FE2740f5E3616155c5b8419
);
}
function getEthPriceFeed() public view returns (AggregatorV3Interface) {
return ethPriceFeed;
}
}
Let's get to the final test, retrieving the latest price from ethPriceFeed. Things get a bit tricky here.
Our Final Test
All of our previous tests thus far have been basic and they all happen in our hardhat environment. But here's the thing, the Chainlink data feeds don't exist in this local hardhat environment.
One really easy solution to this is to fork the Ethereum Blockchain, this simply copies the state of the main net so we can have access to all deployed contracts locally.
Now that that's out of the way, let's add our final test to test/priceFeed.ts:
describe("Price Feed", () => {
// --- Previous Code ---
it("Returns the latest price of Ether", async () => {
expect(await priceFeed.getLatestPrice()).not.be.null;
});
}
Run the yarn hardhat test command again to get a failing test. It fails because getLatestPrice() isn't defined on our PriceFeed.sol file so let's fix that by adding this function to it:
contract PriceFeed {
// --- Previous Code ---
/**
* This function calls the latestRoundData function defined in the
* AggregatorV3Interface.sol file. You can read more about it here:
* https://docs.chain.link/docs/get-the-latest-price/
*
* We're only making use of the price and timestamp being returned.
*/
function getLatestPrice() public view returns (int) {
(, int price, , uint timeStamp, ) = ethPriceFeed.latestRoundData();
// if the round is not complete yet, timestamp is 0
require(timeStamp > 0, "round not complete");
// Uncomment this to see the current price (USD) on your terminal
// console.logInt(price / 10**8);
return price;
}
}
Running yarn hardhat test causes our test to fail once again but this time we get a different error:
In summary, this error is hardhat's way of telling us that nothing is returned and that our code isn't running as expected. Let's fork the mainnet so we can finally make this test green!
Modify hardhat.config.ts to look like this:
import { HardhatUserConfig } from "hardhat/config";
import "dotenv/config";
import "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox";
const ALCHEMY_MAINNET_URL = process.env.ALCHEMY_MAINNET_URL;
const config: HardhatUserConfig = {
solidity: "0.8.9",
networks: {
hardhat: { forking: { url: ALCHEMY_MAINNET_URL! } },
},
};
export default config;
Now run the test command again and viola, it's green!
A value was returned from the Aggregator contract, hence the test passed. And that is how to get price in a decentralized manner.
Thanks for making it to the end, here's the repo to the project. Constructive criticism is always welcome, let me know your thoughts in the comments. Have a great day!

Posted on September 24, 2022
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.
](https://media.dev.to/dynamic/image/width=800%2Cheight=%2Cfit=scale-down%2Cgravity=auto%2Cformat=auto/https%3A%2F%2Fdev-to-uploads.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fuploads%2Farticles%2Fr11bcxkscfea8l45a9qz.png)






