Karan Pratap Singh
Posted on June 23, 2021

What is go fiber?
Fiber is a web framework heavily inspired by Express and that makes it perfect to work with for node developers.
It is built on top of Fasthttp engine, here are some benchmarks. It also has quite a low memory allocation overhead. For example while writing this article it only took around only ~16mb of memory, which was amazing!
In this article let's implement very simple mock api routes to get a feel of the Fiber framework
The code from the article is available in this repository
Getting started
You can install go directly on your system by installing the binary from go docs https://golang.org/doc/install
(optional)
Personally, I like to use docker so I don't have to install anything on my system
Let's pull the golang docker image
docker pull golang
Create your project directory
mkdir go-mock-api
cd go-mock-api
Now we'll bind the port 4000 and mount the current directory (your go project dir) as volume and run our golang image
docker run -itd -p 4000:4000 --name golang -v "$(pwd):/app" golang
Let's run and connect to our running golang container
docker exec -it -w /app golang bash
This should drop us into the golang docker image. Now let's check the version of go and get started
go version
Note: if you're using docker, all the step below are executed inside the golang container
Installation
Let initialise an api module
go mod init api
Install fiber
go get -u github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2
Let's create api.go with a sample hello world server on port 4000 as shown in the repository's readme.
package main
import "github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/", func(ctx *fiber.Ctx) error {
return ctx.SendString("Hello, World!")
})
app.Listen(":4000")
}
Development
Reflex helps with live reload for Go apps, which is great for development. It is quite similar to nodemon, alternatively, you can simply use go run command to run your program.
go get github.com/cespare/reflex
Let's start!
reflex -g '*.go' go run api.go --start-service
Starting service...
┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Fiber v2.13.0 │
│ http://127.0.0.1:4000 │
│ (bound on host 0.0.0.0 and port 4000) │
│ │
│ Handlers ............. 2 Processes ........... 1 │
│ Prefork ....... Disabled PID .............. 3315 │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Note: Make sure you have PATH exported in your .bashrc or .zshrc file as export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/go/bin/
Now you should be seeing your code running and it should auto reload when you change something, without having to re-run your go program!
Creating a GET route
Let's import fiber
import "github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
Add a user route to the main function
app.Get("/user", getUserHandler)
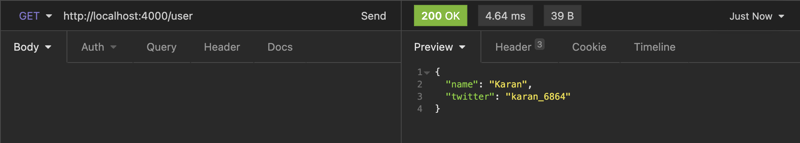
Let's add getUserHandler which will handle the request. Here we will return a mock user.
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Twitter string `json:"twitter"`
}
func getUserHandler(ctx *fiber.Ctx) error {
user := User{
Name: "Karan",
Twitter: "karan_6864",
}
return ctx.Status(fiber.StatusOK).JSON(user)
}
Creating a POST route
Similarly, let's add a post route to the main function
app.Post("/user/create", createUserHandler)
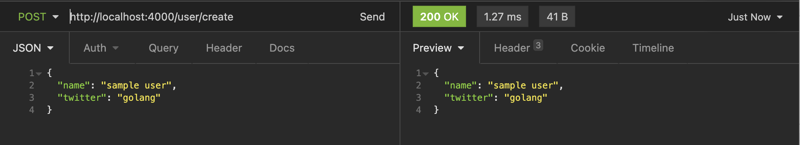
Let's add a createUserHandler which will handle the request. Here we will simply parse the body and send it back in the response
func createUserHandler(ctx *fiber.Ctx) error {
body := new(User)
err := ctx.BodyParser(body)
if err != nil {
ctx.Status(fiber.StatusBadRequest)
return err
}
user := User{
Name: body.Name,
Twitter: body.Twitter,
}
return ctx.Status(fiber.StatusOK).JSON(user)
}
Middleware
Let's add logging middleware that comes with fiber
import (
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2/middleware/logger"
)
Add this middleware to main function
app.Use(logger.New())
This should give us some logs as shown below
12:04:01 | 200 | 1ms | 172.17.0.1 | GET | /user
12:04:27 | 200 | 0s | 172.17.0.1 | POST | /user/create
We can define custom middlewares as well
app.Use(func(ctx *fiber.Ctx) error {
fmt.Println("Sample middleware")
return ctx.Next()
})
Router
We can organize our routes with Group function, very similar to how we do routing in express.
userApi := app.Group("/user")
userApi.Get("/", getUserHander)
userApi.Post("/create", createUserHandler)
Serving static file
Let's assume we're trying to server public folder, we can simply use the Static function like below
app.Static("/", "./public")
Let's try it out!
Here's our final api.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2/middleware/logger"
)
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Twitter string `json:"twitter"`
}
func getUserHander(ctx *fiber.Ctx) error {
user := User{
Name: "Karan",
Twitter: "karan_6864",
}
return ctx.Status(fiber.StatusOK).JSON(user)
}
func createUserHandler(ctx *fiber.Ctx) error {
body := new(User)
err := ctx.BodyParser(body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
ctx.Status(fiber.StatusBadRequest)
return err
}
user := User{
Name: body.Name,
Twitter: body.Twitter,
}
return ctx.Status(fiber.StatusOK).JSON(user)
}
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Use(logger.New())
userApi := app.Group("/user")
userApi.Get("/", getUserHander)
userApi.Post("/create", createUserHandler)
app.Listen(":4000")
}
I'm using Insomnia to test out the mock endpoints
Get user
Create user
Feel to reachout to me on twitter if you face any issues.
Feedback is always welcome, Have fun!

Posted on June 23, 2021
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.
Related

November 7, 2024

November 5, 2024

October 30, 2024