What's new with JavaScript in 2020 - Ecmascript 2020/ES11

Michael Richardson
Posted on October 21, 2022

Background
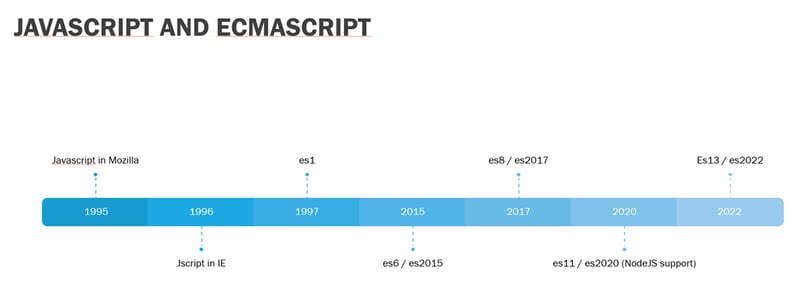
Before ecmaScript came Javascript. The creator Brendan Eich set out to create a language like, but simpler than Java. Javascript was originally created for Netscape and before it went down, a project was started to formalize the language and that became ecmascript. What we know today as Javascript, is really vendor-specific implementations of ecmascript.
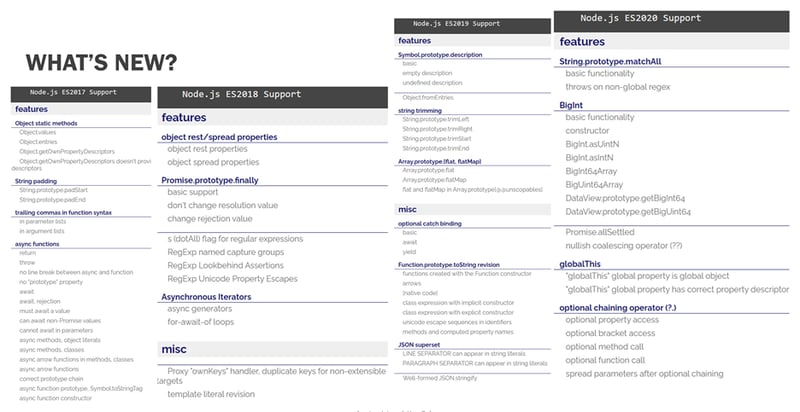
Ecmascript didn't really gain traction until version 6 and it has continued to evolve since. Support for a given version is entirely dependent on the environment such as node vs browser, which browser, which version of that browser and such. Right now es version 13 also known as es2022 is stable, BUT support for it in Node isn't stable until version 17.9.1 (97% coverage). Since we are still on NodeJS 14, ecmaScript support is limited currently to es11 or es2020. When we make the move to Node 18.x, then we will have support for es version 13 aka es2022.
Hopefully you have some idea of the versions and timelines now, but why does it matter? Because each new ecmaScript version defines new features. As vendors improve support for that new version, they are exposed to developers in their products (like browsers and NodeJS). I show you all these now to give you an idea how many new features have released since es8/2017. I can't cover even a majority of them, but today I'm going to briefly highly some that may prove helpful in providing more stable code, code that's easier to read (and write tests for nod) or help you avoid anti-patterns or just write simpler code.
Nullish coalescing
A bit like using OR to return the first/left-most non-null, non-empty value; nullish coalescing returns the first/left-most non-null value, even if it's empty.
const response = {
settings: {
nullValue: null , height: 400, animationDuration: 0, headerText: '', showSplashScreen: false
},
};
const undefinedValue = response.settings.undefinedValue ?? 'some other default' ; // result: 'some other default'
const nullValue = response.settings.nullValue ?? 'some other default' ; // result: 'some other default'
const headerText = response.settings.headerText ?? 'Hello, world!' ; // result: ''
const animationDuration = response.settings.animationDuration ?? 300; // result: 0
const showSplashScreen = response.settings.showSplashScreen ?? true ; // result: false
const x = '' || 'x'; // result: 'x'
const x = '' ?? 'x'; // result: ''
Optional Chaining
When looking for a property value that's deep in a tree-like structure, one often has to check whether intermediate nodes exist before you can check for the deeper value. Optional chaining simplifies this by using a question-mark before the dot-notation.
const user = {};
// Before:
var street = user.address.street; // Error: cannot read properties of undefined var street = user.address && user.address.street; // undefined
// Now:
var street = user?.address?.street; // undefined
Logical assignment operator
This is a convenience operators, inspired by Ruby's. Javascript already has a dozen mathematical assignment operators, but we didn't have ones for the often used logical operators.
// Ok, but could trigger setter.
opts.foo = opts.foo ?? 'bar'
// No setter, but 'feels wrong' to write.
opts.baz ?? (opts.baz = 'qux');
// Setters are not needlessly called.
opts.foo ??= 'bar'
// No repetition of `opts.baz`.
opts.baz ??= 'qux';
// This always logs "setter called"
obj.x += 1;
assert.equal(obj.x, 1);
// Logical operators do not call setters unnecessarily
// This will not log.
obj.x ||= 2;
assert.equal(obj.x, 1);
// But setters are called if the operator does not short circuit
// "setter called"
obj.x &&= 3;
assert.equal(obj.x, 3)
Object rest/spread
ECMAScript 6 introduces rest elements for ARRAY destructuring assignment and spread elements for ARRAY literals. With es11, we get rest properties for OBJECT destructuring assignment and spread properties for OBJECT literals.
let { x, y, ...z } = { x: 1, y: 2, a: 3, b: 4 };
x; // 1
y; // 2
z; // { a: 3, b: 4 }
let n = { x, y, ...z };
n; // { x: 1, y: 2, a: 3, b: 4 }
Conclusion
ECMAScript is constantly evolving and the more current your environment (latest Node.js, browser, or other client), the more features you'll have access to. Be sure to keep an eye on which version of eslint you want to target by watching resources like https://node.green/ and https://caniuse.com/?search=es11.

Posted on October 21, 2022
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.
Related

November 30, 2024
November 30, 2024