Como identificar se a automação está executando localmente ou no BotCity Orquestrador?

Morganna
Posted on March 6, 2024

A dúvida surgiu
Enquanto estávamos em nossa live coding desenvolvendo uma automação com Python e fazendo integração com e-mail e Google Sheets, surgiu uma dúvida:
Como identificar se a automação está executando localmente ou no BotCity Orquestrador?
Essa dúvida surgiu por causa da seguinte situação: quando estamos executando nossa automação localmente, ou seja, em nosso computador ou máquina virtual, e queremos conectá-la com o BotCity Orquestrador, precisamos utilizar o BotCity Maestro SDK para fazer login na plataforma. Mas quando fazemos deploy no Orquestrador, esse trecho de código para o login não precisa existir.
Exemplo prático
Criei um robô seguindo a documentação do framework web para exemplo. Abaixo temos o código principal:
# Import for the Web Bot
from botcity.web import WebBot, Browser, By
# Import for integration with BotCity Maestro SDK
from botcity.maestro import *
# Disable errors if we are not connected to Maestro
BotMaestroSDK.RAISE_NOT_CONNECTED = False
def main():
# Runner passes the server url, the id of the task being executed,
# the access token and the parameters that this task receives (when applicable).
maestro = BotMaestroSDK.from_sys_args()
## Fetch the BotExecution with details from the task, including parameters
execution = maestro.get_execution()
print(f"Task ID is: {execution.task_id}")
print(f"Task Parameters are: {execution.parameters}")
bot = WebBot()
# Configure whether or not to run on headless mode
bot.headless = False
# Uncomment to change the default Browser to Firefox
# bot.browser = Browser.FIREFOX
# Uncomment to set the WebDriver path
# bot.driver_path = "<path to your WebDriver binary>"
# Opens the BotCity website.
bot.browse("https://www.botcity.dev")
# Implement here your logic...
...
# Wait 3 seconds before closing
bot.wait(3000)
# Finish and clean up the Web Browser
# You MUST invoke the stop_browser to avoid
# leaving instances of the webdriver open
bot.stop_browser()
# Uncomment to mark this task as finished on BotMaestro
# maestro.finish_task(
# task_id=execution.task_id,
# status=AutomationTaskFinishStatus.SUCCESS,
# message="Task Finished OK."
# )
def not_found(label):
print(f"Element not found: {label}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
E assim fica o código do requirements.txt:
botcity-framework-web>=0.8.0,<1.0
botcity-maestro-sdk>=0.3.3,<1.0
O que eu fiz para poder executar esse código, foi descomentar a linha:
bot.browser = Browser.FIREFOX
E adicionar o geckodriver na configuração do WebDriver, deixando-o na pasta resources:
bot.driver_path = r"resources\geckodriver.exe"
Esse bot é apenas um exemplo e o que ele faz ao ser executado é abrir o navegador Firefox (poderia ter sido o Chrome, Edge, entre outros) com o site da BotCity e, depois de três segundos, fecha o navegador.
Conexão com BotCity Orquestrador
Se você precisar se conectar com a plataforma para orquestração, você precisará adicionar o seguinte código para fazer login no BotCity Orquestrador:
maestro.login(
server='MAESTRO_SERVER',
login='MAESTRO_LOGIN',
key='MAESTRO_KEY'
)
Por serem dados sensíveis, uma saída para ocultar os dados é utilizando dotenv do Python e o OS. Para isso, basta importar da seguinte forma:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
...
def main():
load_dotenv()
...
E no arquivo requirements.txt precisa adicionar a biblioteca dotenv:
botcity-framework-web>=0.8.0,<1.0
botcity-maestro-sdk>=0.3.3,<1.0
python-dotenv
Além disso também é necessário termos um arquivo chamado .env, pois é de lá que o código buscará as informações. E esse arquivo ficará da seguinte forma:
MAESTRO_SERVER = "coloque o server aqui"
MAESTRO_LOGIN = "coloque o login aqui"
MAESTRO_KEY = "coloque a key aqui"
Essas informações ficam disponíveis em Dev. Environment, no BotCity Orquestrador.
OBS: É importante lembrar de não disponibilizar o .env ao versionar em plataformas como o GitHub, Gitlab, entre outras. Para facilitar, adicione .env ao arquivo .gitignore.
Qual a diferença entre o ambiente local e o orquestrador
Quando executamos nossa automação dentro do Orquestrador, uma tarefa é criada, atrelada a automação que fizemos o deploy, então por ele nós temos o ID da tarefa (ou task_id). Já no ambiente local, não temos essa informação.
Como validar em qual ambiente está sendo executado
Então podemos, por exemplo, fazer a seguinte validação: se task_id for igual a 0, estamos executando localmente e precisamos fazer o processo de login com o Orquestrador. Caso contrário, o task_id existe e, então, não precisamos fazer o login.
...
maestro = BotMaestroSDK.from_sys_args()
## Fetch the BotExecution with details from the task, including parameters
execution = maestro.get_execution()
if(execution.task_id == 0):
print("Running locally so we need to login to BotCity Orchestrator.")
maestro.login(
server=os.getenv('MAESTRO_SERVER'),
login=os.getenv('MAESTRO_LOGIN'),
key=os.getenv('MAESTRO_KEY')
)
else:
print("Running with BotCity Orchestrator.")
...
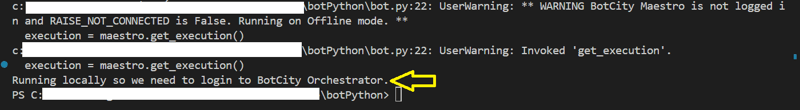
Execução local
Ao testar a execução do robô localmente, percebemos que retorna a mensagem correta no terminal:
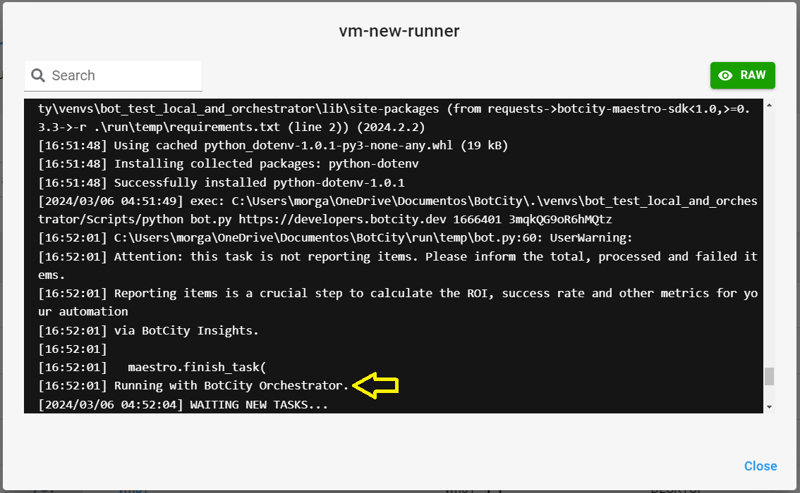
Execução no Orquestrador
Ao testar a execução do robô no Orquestrador, percebemos que retorna a mensagem correta no terminal:
Código completo
Caso queira validar como ficou o código principal completo, segue abaixo:
# Import for the Web Bot
from botcity.web import WebBot, Browser, By
# Import for integration with BotCity Maestro SDK
from botcity.maestro import *
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
# Disable errors if we are not connected to Maestro
BotMaestroSDK.RAISE_NOT_CONNECTED = False
def main():
load_dotenv()
# Runner passes the server url, the id of the task being executed,
# the access token and the parameters that this task receives (when applicable).
maestro = BotMaestroSDK.from_sys_args()
## Fetch the BotExecution with details from the task, including parameters
execution = maestro.get_execution()
if(execution.task_id == 0):
print("Running locally so we need to login to BotCity Orchestrator.")
maestro.login(
server=os.getenv('MAESTRO_SERVER'),
login=os.getenv('MAESTRO_LOGIN'),
key=os.getenv('MAESTRO_KEY')
)
else:
print("Running with BotCity Orchestrator.")
bot = WebBot()
# Configure whether or not to run on headless mode
bot.headless = False
# Uncomment to change the default Browser to Firefox
bot.browser = Browser.FIREFOX
# Uncomment to set the WebDriver path
bot.driver_path = r"resources\geckodriver.exe"
# Opens the BotCity website.
bot.browse("https://www.botcity.dev")
# Implement here your logic...
...
# Wait 3 seconds before closing
bot.wait(3000)
# Finish and clean up the Web Browser
# You MUST invoke the stop_browser to avoid
# leaving instances of the webdriver open
bot.stop_browser()
# Uncomment to mark this task as finished on BotMaestro
maestro.finish_task(
task_id=execution.task_id,
status=AutomationTaskFinishStatus.SUCCESS,
message="Task Finished OK."
)
def not_found(label):
print(f"Element not found: {label}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
O que achou?
Espero que tenha curtido a dica e possa adaptá-la de acordo com a necessidade da sua execução. Qualquer dúvida, basta entrar em contato pela nossa comunidade.

Posted on March 6, 2024
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.