C# Stacks

Andres Ramirez
Posted on March 28, 2024

A stack follows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) or First In, Last Out (FILO) order, which means that the last element added to the stack is the first one to be removed.
To manage a stack, a pointer to the top is maintained, allowing access only to the top element.
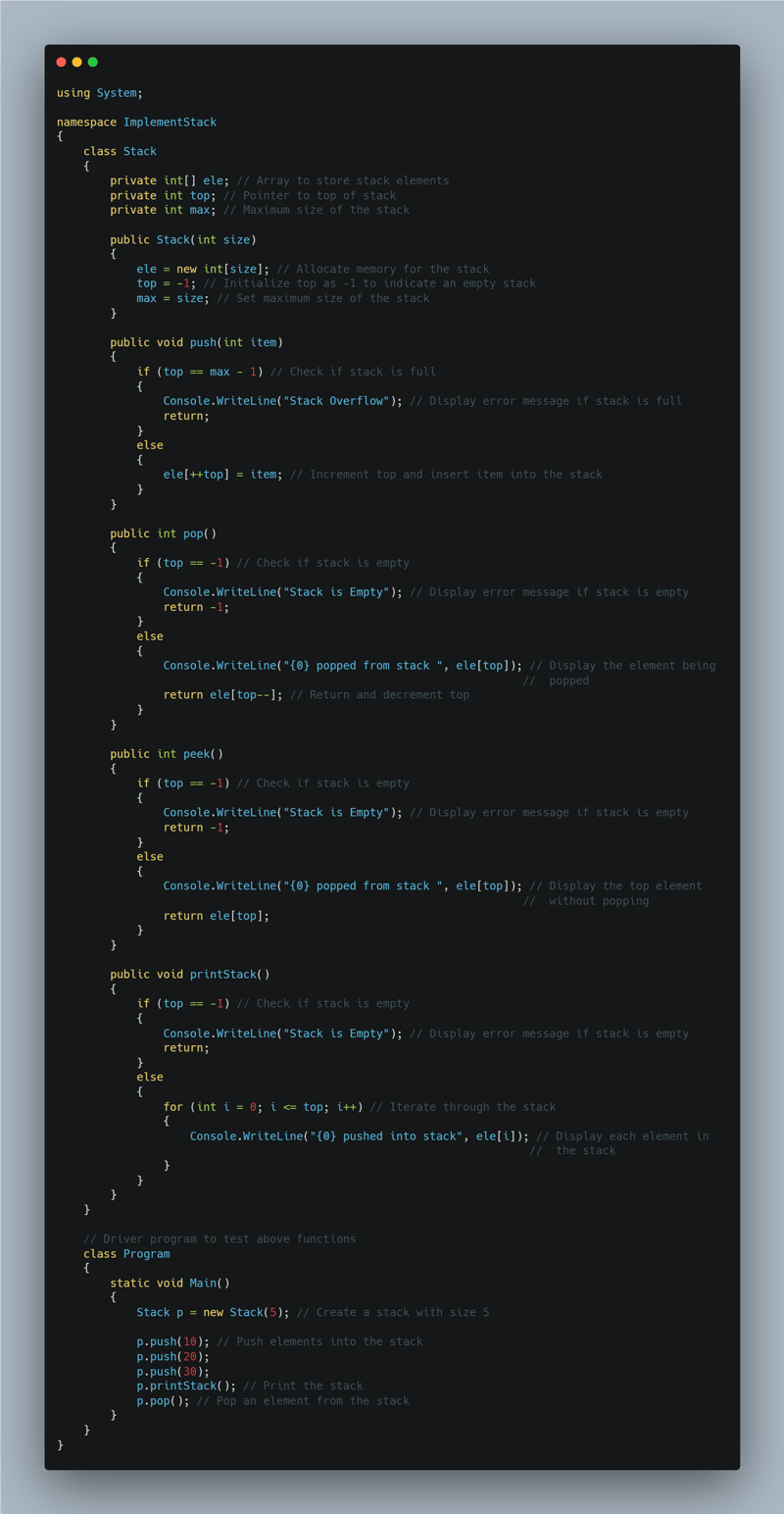
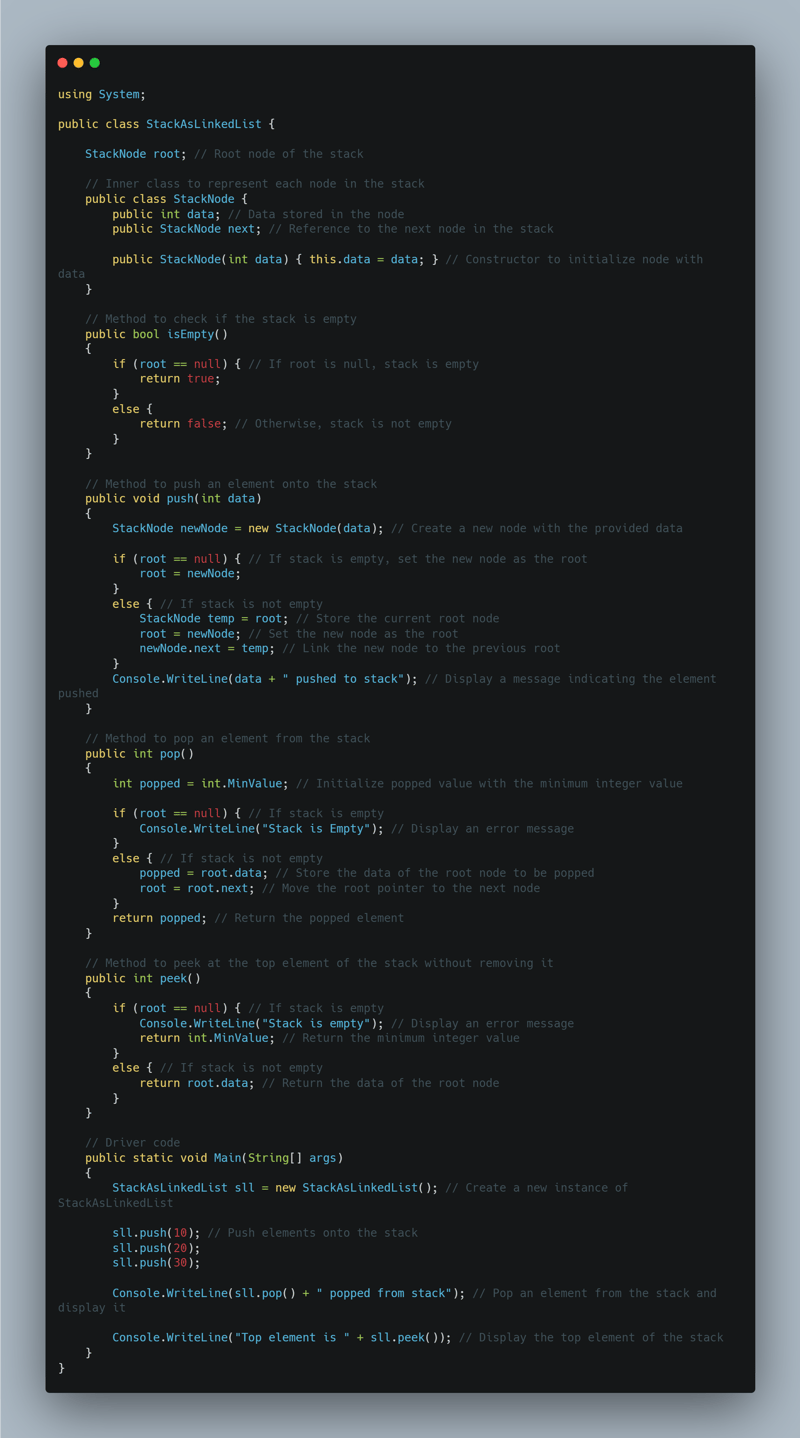
Basic operations include push, pop, peek, isempty, top, and size.
Two types of stacks exist: dynamic (adjusting size dynamically) and static (fixed size).
Stacks can be implemented using arrays or linked lists.
Implementing Stack using Arrays
Implementing Stack a Linked List
Implement a stack using singly linked list
using System;
// Create Stack Using Linked list
public class StackUsingLinkedlist {
// A linked list node
private class Node {
// integer data
public int data;
// reference variable Node type
public Node link;
}
// create global top reference variable
Node top;
// Constructor
public StackUsingLinkedlist() { this.top = null; }
// Utility function to add
// an element x in the stack
// insert at the beginning
public void push(int x)
{
// create new node temp and allocate memory
Node temp = new Node();
// check if stack (heap) is full.
// Then inserting an element
// would lead to stack overflow
if (temp == null) {
Console.Write("\nHeap Overflow");
return;
}
// initialize data into temp data field
temp.data = x;
// put top reference into temp link
temp.link = top;
// update top reference
top = temp;
}
// Utility function to check if
// the stack is empty or not
public bool isEmpty() { return top == null; }
// Utility function to return
// top element in a stack
public int peek()
{
// check for empty stack
if (!isEmpty()) {
return top.data;
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
}
// Utility function to pop top element from the stack
public void pop() // remove at the beginning
{
// check for stack underflow
if (top == null) {
Console.Write("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
// update the top pointer to
// point to the next node
top = (top).link;
}
public void display()
{
// check for stack underflow
if (top == null) {
Console.Write("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
else {
Node temp = top;
while (temp != null) {
// print node data
Console.Write(temp.data);
// assign temp link to temp
temp = temp.link;
if(temp != null)
Console.Write(" -> ");
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public class GFG {
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// create Object of Implementing class
StackUsingLinkedlist obj
= new StackUsingLinkedlist();
// insert Stack value
obj.push(11);
obj.push(22);
obj.push(33);
obj.push(44);
// print Stack elements
obj.display();
// print Top element of Stack
Console.Write("\nTop element is {0}\n", obj.peek());
// Delete top element of Stack
obj.pop();
obj.pop();
// print Stack elements
obj.display();
// print Top element of Stack
Console.Write("\nTop element is {0}\n", obj.peek());
}
}
💖 💪 🙅 🚩

Andres Ramirez
Posted on March 28, 2024
Join Our Newsletter. No Spam, Only the good stuff.
Sign up to receive the latest update from our blog.